The OpenStack Board spent several hours (yes, hours) discussing interoperability related topics at the last board meeting. Fundamentally, the community benefits when uses can operate easily across multiple OpenStack deployments (their own and/or public clouds).
Cloud interoperability: the ability to transfer workloads between systems without changes to the deployment operations management infrastructure.
This is NOT hybrid (which I defined as a workload transparently operating in multiple systems); however it is a prereq to achieve scalable hybrid operation.
Interoperability matters because the OpenStack value proposition is all about creating a common platform. IT World does a good job laying out the problem (note, I work for Dell). To create sites that can interoperate, we have to some serious lifting:
- Continue to standardize APIs
- Create tests that validate the APIs
- Agree to common operations practices
- Provide clear upgrade processes and tolerances to clients using different API versions
At the OpenStack Summit, there are multiple chances to engage on this. I’m moderating a panel about Interop and also sharing a session about the highly related topic of Reference Architectures with Monty Tayor.
The Interop Panel (topic description here) is Tuesday @ 5:20pm. If you join, you’ll get to see me try to stump our awesome panelists
- Jonathan LaCour, DreamHost
- Troy Toman, Rackspace
- Bernard Golden, Enstratius
- Monty Taylor, OpenStack Board (and HP)
- Peter Pouliot, Microsoft
PS: Oh, and I’m also talking about DevOps Upgrades Patterns during the very first session (see a preview).

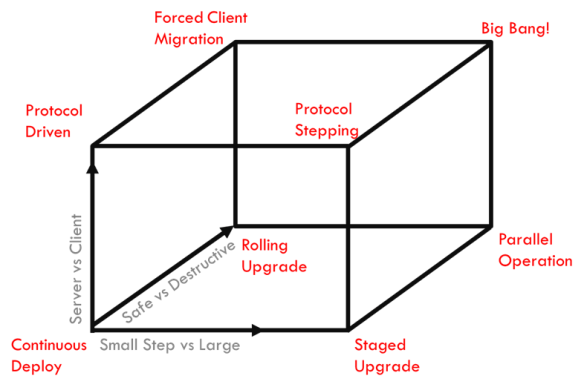

 I’m certain that the
I’m certain that the 


 I also see that community driven work is positioning Crowbar to break beyond being platforms for OpenStack and Apache Hadoop solutions that pay the bills for
I also see that community driven work is positioning Crowbar to break beyond being platforms for OpenStack and Apache Hadoop solutions that pay the bills for  During last week’s
During last week’s  Curious about
Curious about  I’m overwhelmed and humbled by the enthusiasm
I’m overwhelmed and humbled by the enthusiasm